Breadfruit is a multipurpose species and all parts of the tree are used. It is an essential component of home gardens and traditional agroforestry systems, creating a lush overstory that shelters a wide range of cultivated and native plants. In the Pacific, breadfruit agroforests have protected mountain slopes from erosion for more than two millennia.
Tree

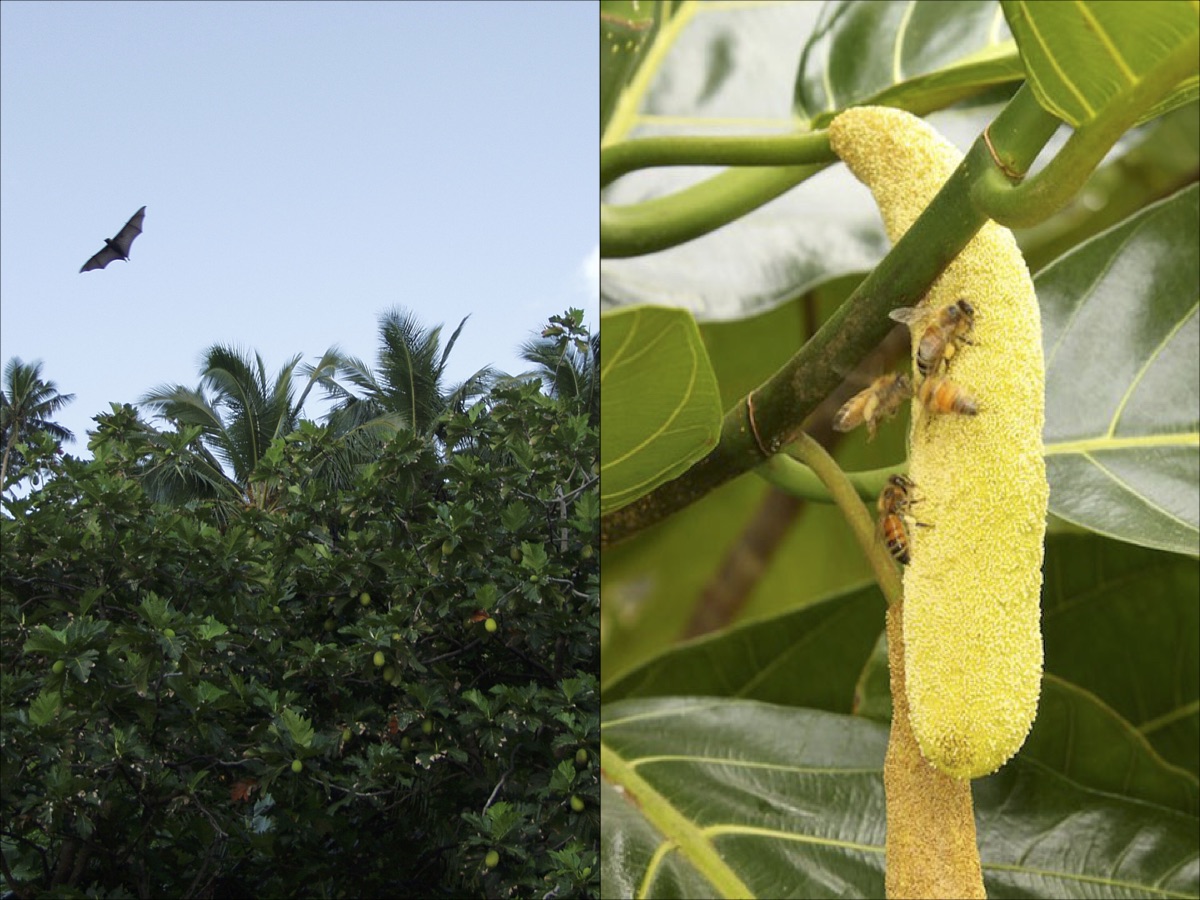
The trees have a beneficial impact on the natural environment creating organic mulch, shade, and a cooler micro-climate beneath the canopy. They give shelter and food to important pollinators and seed dispersers such as honeybees, birds, and fruit bats. A breadfruit tree yields food, construction materials, medicine, cordage, glue, insect repellent, and animal feed.

Timber
The trunk of a breadfruit tree may be as large as 2 meters in diameter and grow to a height of 4 meters before branching. The wood is light and durable with a light golden color that darkens with age. It is used for the construction of houses and canoes because it resists termites and marine worms. The hulls of outrigger canoes are often fashioned from a single log and are still made in parts of Micronesia and Melanesia. The wood is carved into attractive bowls, statues, handicrafts, furniture, and other items. Older trees are an important source of firewood, especially on the atoll islands.
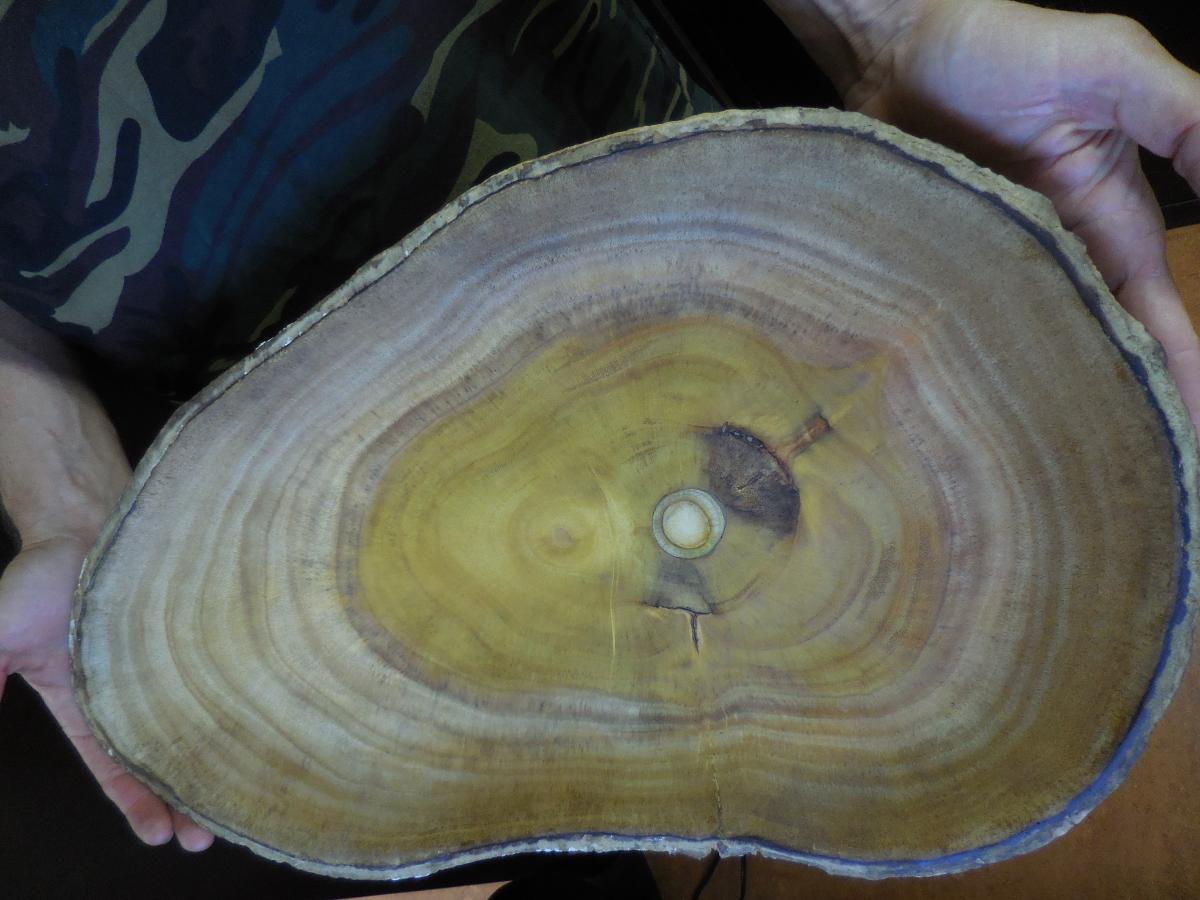
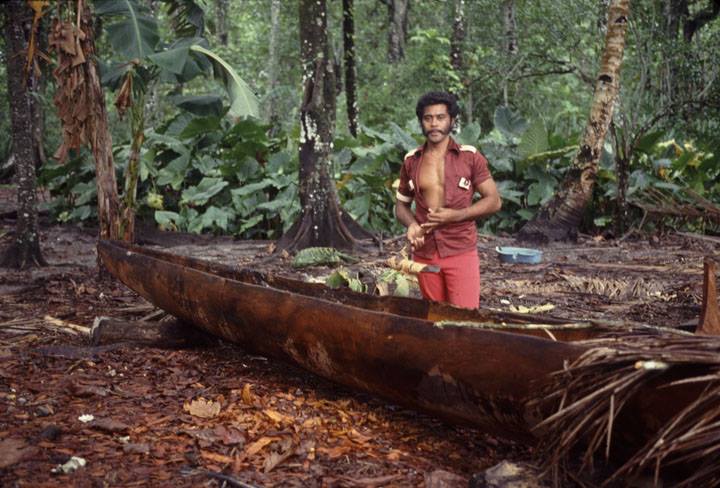



Bark
The inner bark, or bast, can be made into bark cloth. In the Pacific, islanders chose branches with new growth and remove the outer bark. After separating the brown outer bark from the white inside bark, the white bark is beaten on a smooth stone to spread it. After the beating process is complete, the bark has become a soft, fibrous cloth that is colored with natural dyes. The inner bark is also traditionally used to make a strong cordage used for building and fishing.
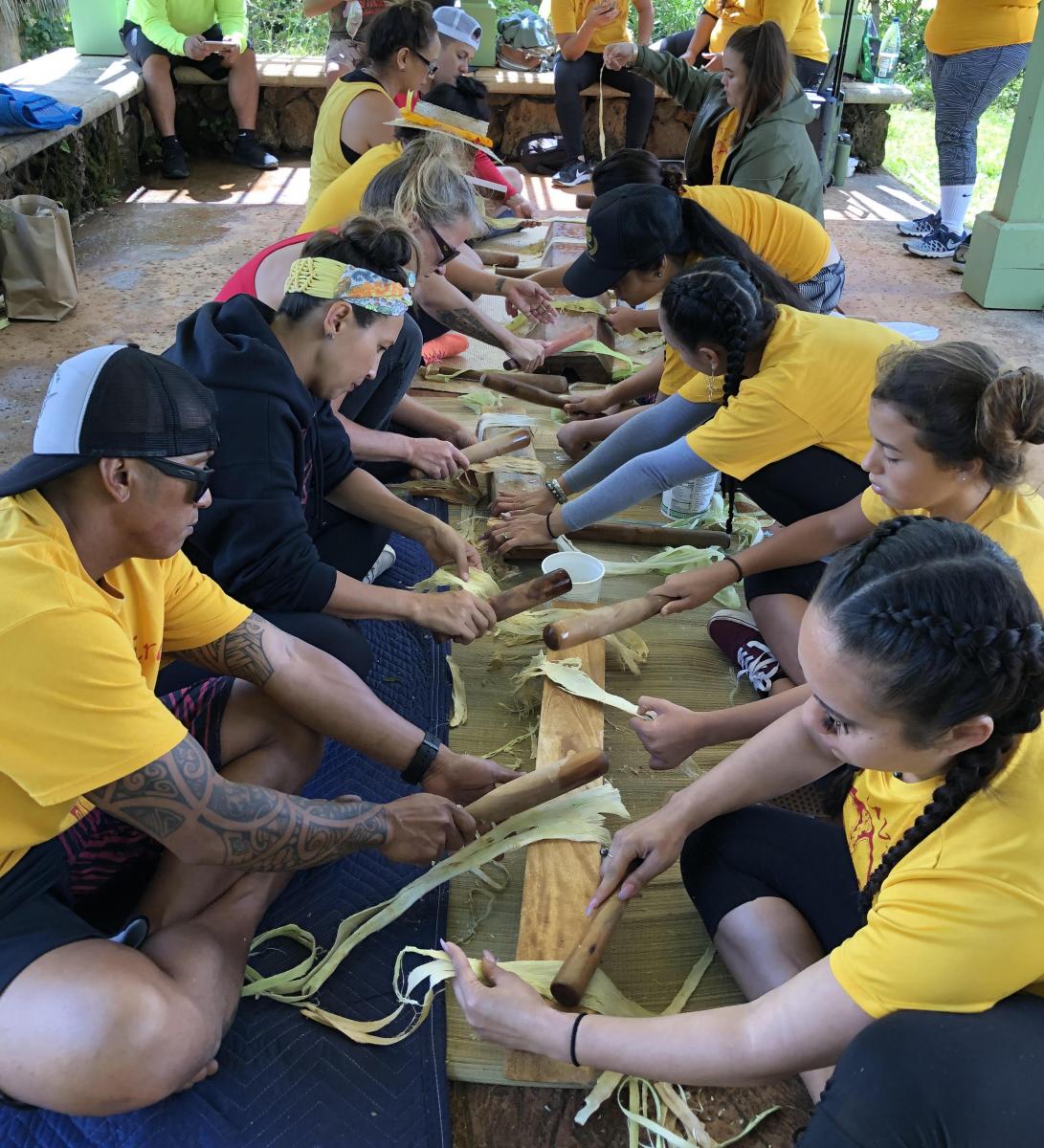
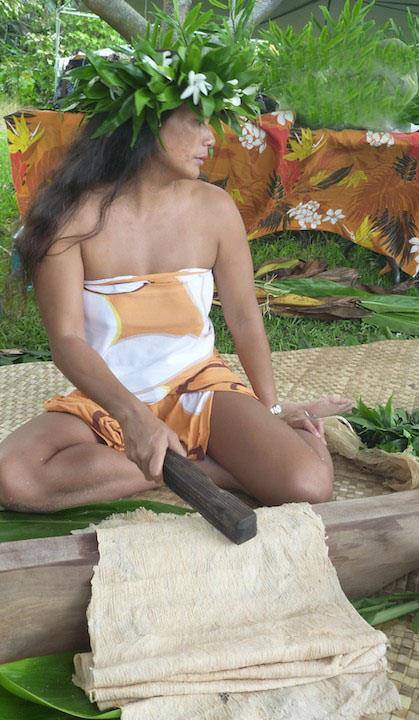
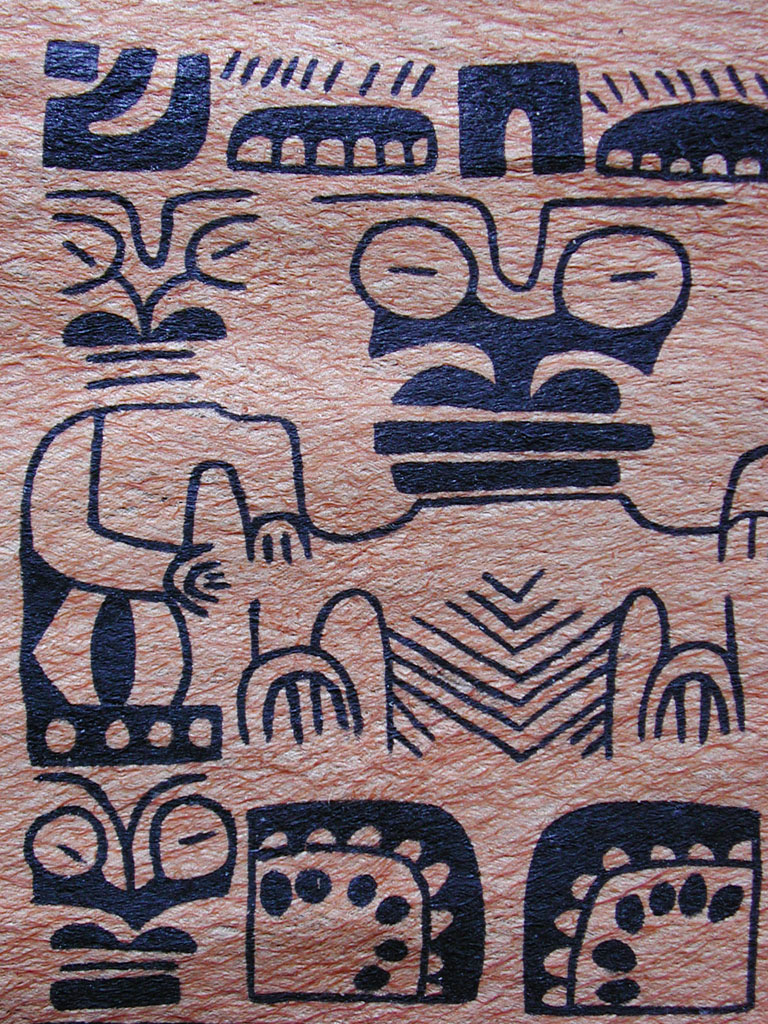



Leaves
The leaves are used as fans, sandpaper for fine woodwork, to wrap foods that are cooked in traditional earth ovens, and as biodegradable plates.
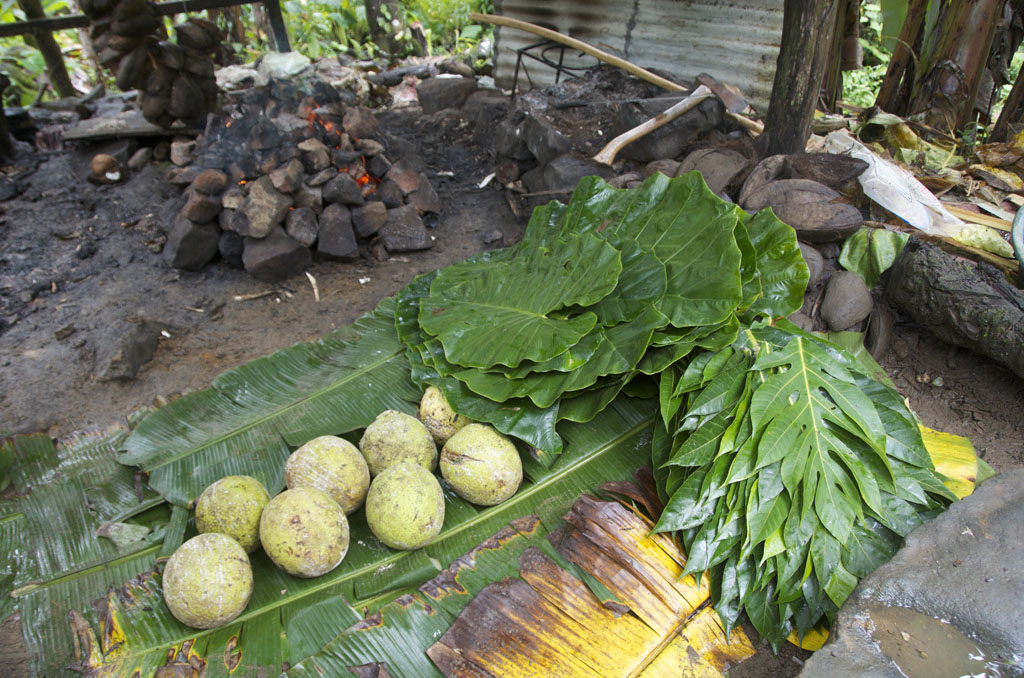


Latex
Sticky white latex (sap) is present in all parts of the tree and has been used for glue, caulk, and even chewing gum. Bees are attracted to and harvest droplets of sap from the surface of the fruit. Bird catchers smeared the latex onto branches to entrap saffron-feathered honeycreepers.

Traditional Medicine
The breadfruit tree was an important part of the native pharmacopoeia in the Pacific Islands. The latex was massaged into the skin to treat broken bones and sprains and bandaged on the spine to relieve sciatica. Crushed leaves are commonly used to treat skin ailments and fungus diseases such as ‘thrush’. Diluted latex, taken internally, treated diarrhea, stomachaches, and dysentery. The sap from the crushed stems of leaves is used to treat ear infections or sore eyes. The root is an astringent and used as a purgative; when macerated it is used as a poultice for skin ailments. The bark is also used to treat headaches in several islands. In the West Indies, the yellowing leaf is brewed into tea and taken to reduce high blood pressure and to relieve asthma. The tea is also thought to control diabetes.
